MinerU Beginner's Guide - Ultimate Open Source PDF Data Extraction Tool
What is MinerU?
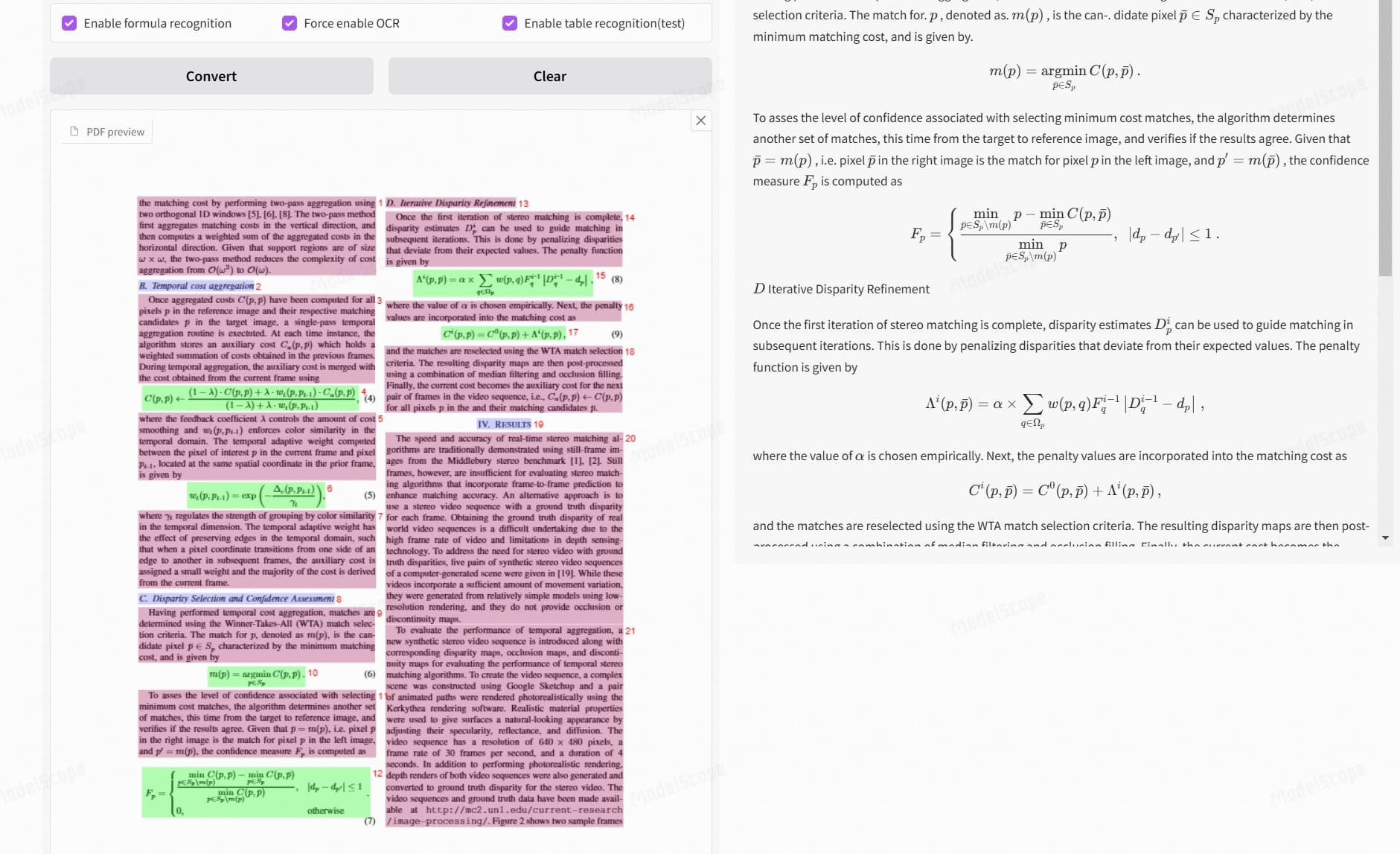
MinerU is a powerful open-source PDF data extraction tool developed by OpenDataLab. It intelligently converts PDF documents into structured data formats, supporting precise extraction of text, images, tables, and mathematical formulas. Whether you’re dealing with academic papers, technical documents, or business reports, MinerU makes it easy.
Key Features
- 🚀 Smart Cleaning - Automatically removes headers, footers, and other distracting content
- 📝 Structure Preservation - Retains the hierarchical structure of the original document
- 🖼️ Multimodal Support - Accurately extracts images, tables, and captions
- ➗ Formula Conversion - Automatically recognizes mathematical formulas and converts them to LaTeX
- 🌍 Multilingual OCR - Supports text recognition in 84 languages
- 💻 Cross-Platform Compatibility - Works on all major operating systems
Multilingual Support
MinerU leverages PaddleOCR to provide robust multilingual recognition capabilities, supporting over 80 languages:
Major Language Support
| Language | Abbreviation | Description | Language | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | ch | Chinese-English mixed | English | en | English |
| Japanese | japan | Japanese | Korean | korean | Korean |
| Russian | ru | Russian | French | fr | French |
| German | german | German | Italian | it | Italian |
| Spanish | es | Spanish | Portuguese | pt | Portuguese |
Special Language Support
| Language Family | Language | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Asian | Traditional Chinese | chinese_cht |
| Asian | Uyghur | ug |
| Asian | Tamil | ta |
| Asian | Telugu | te |
| Asian | Nepali | ne |
| European | Serbian | latin/cyrillic |
| European | Croatian | hr |
| European | Irish | ga |
| European | Hungarian | hu |
| Middle Eastern | Arabic | ar |
| Middle Eastern | Persian | fa |
| Middle Eastern | Urdu | ur |
| Middle Eastern | Kurdish | ku |
Usage
When processing documents, you can optimize recognition accuracy by specifying the language parameter:
magic-pdf -p paper.pdf -o output -m auto --lang chNote: Selecting the correct language can significantly improve recognition accuracy. For mixed language documents, it is recommended to use the automatic detection mode.
Effect Demonstration
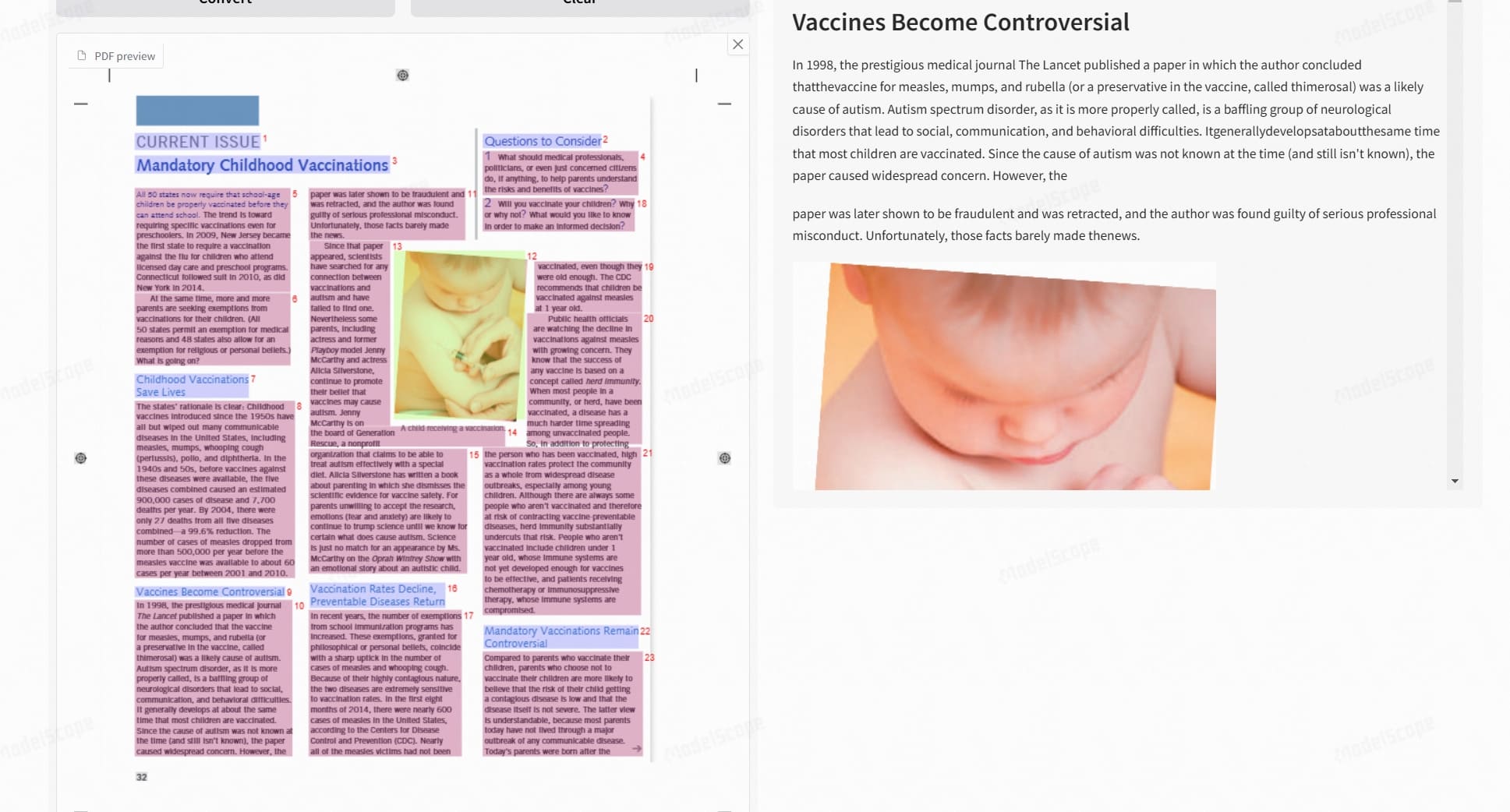
Quick Start
Online Experience
If you prefer not to install, you can experience it directly through the following platforms:
- HuggingFace - Test Version
- ModelScope - Test Version
Local Installation
Basic Environment Configuration
# Create a virtual environment
conda create -n MinerU python=3.10
conda activate MinerU
# Install core packages
pip install -U magic-pdf[full] --extra-index-url https://wheels.myhloli.comBasic Usage
# Process a single file
magic-pdf -p paper.pdf -o output -m auto
# Batch process a folder
magic-pdf -p papers_dir -o output -m autoAdvanced Features
GPU Acceleration Configuration
如果您的显卡显存大于等于8GB,可以按照以下步骤启用CUDA加速:
1. Modify Configuration File
Find the magic-pdf.json file in your user directory and modify the “device-mode” value:
{
"device-mode": "cuda"
}2. Enable CUDA Acceleration
Run the following command to test the CUDA acceleration effect:
magic-pdf -p small_ocr.pdf -o ./output提示: CUDA加速是否生效可以根据log中输出的各个阶段cost耗时来判断。通常情况下,
layout detection cost和mfr time应提速10倍以上。
3. OCR Acceleration Configuration
To enable CUDA acceleration for OCR, you need to install paddlepaddle-gpu:
# Install paddlepaddle-gpu, OCR acceleration will be enabled automatically
python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==3.0.0b1 -i https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/packages/stable/cu118/
# Test OCR acceleration effect
magic-pdf -p small_ocr.pdf -o ./output提示: OCR加速生效后,log中的
ocr cost耗时应该减少10倍以上。
Table Recognition Enhancement
The latest version integrates the RapidTable table recognition engine:
- ⚡ Recognition speed increased by 10 times
- 🎯 Higher recognition accuracy
- 💾 Lower resource consumption
API Integration Development
MinerU provides flexible Python APIs, here is a complete usage example:
import os
from loguru import logger
from magic_pdf.pipe.UNIPipe import UNIPipe
from magic_pdf.pipe.OCRPipe import OCRPipe
from magic_pdf.pipe.TXTPipe import TXTPipe
from magic_pdf.rw.DiskReaderWriter import DiskReaderWriter
def pdf_parse_main(
pdf_path: str,
parse_method: str = 'auto',
model_json_path: str = None,
is_json_md_dump: bool = True,
output_dir: str = None
):
"""
Execute the process from pdf to json and md
:param pdf_path: Path to the .pdf file
:param parse_method: Parsing method, supports auto, ocr, txt, default auto
:param model_json_path: Path to an existing model data file
:param is_json_md_dump: Whether to save parsed data to json and md files
:param output_dir: Output directory path
"""
try:
# Prepare output path
pdf_name = os.path.basename(pdf_path).split(".")[0]
if output_dir:
output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, pdf_name)
else:
pdf_path_parent = os.path.dirname(pdf_path)
output_path = os.path.join(pdf_path_parent, pdf_name)
output_image_path = os.path.join(output_path, 'images')
image_path_parent = os.path.basename(output_image_path)
# Read PDF file
pdf_bytes = open(pdf_path, "rb").read()
# Initialize writer
image_writer = DiskReaderWriter(output_image_path)
md_writer = DiskReaderWriter(output_path)
# Select parsing method
if parse_method == "auto":
jso_useful_key = {"_pdf_type": "", "model_list": []}
pipe = UNIPipe(pdf_bytes, jso_useful_key, image_writer)
elif parse_method == "txt":
pipe = TXTPipe(pdf_bytes, [], image_writer)
elif parse_method == "ocr":
pipe = OCRPipe(pdf_bytes, [], image_writer)
else:
logger.error("unknown parse method, only auto, ocr, txt allowed")
return
# Execute processing flow
pipe.pipe_classify() # Document classification
pipe.pipe_analyze() # Document analysis
pipe.pipe_parse() # Content parsing
# Generate output content
content_list = pipe.pipe_mk_uni_format(image_path_parent)
md_content = pipe.pipe_mk_markdown(image_path_parent)
# Save results
if is_json_md_dump:
# Save model results
md_writer.write(
content=json.dumps(pipe.model_list, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4),
path=f"{pdf_name}_model.json"
)
# Save content list
md_writer.write(
content=json.dumps(content_list, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4),
path=f"{pdf_name}_content_list.json"
)
# Save Markdown
md_writer.write(
content=md_content,
path=f"{pdf_name}.md"
)
except Exception as e:
logger.exception(e)
# Usage example
if __name__ == '__main__':
pdf_path = "demo.pdf"
pdf_parse_main(
pdf_path=pdf_path,
parse_method="auto",
output_dir="./output"
)Note: The above code demonstrates a complete processing flow, including:
- Support for multiple parsing methods (auto/ocr/txt)
- Automatically create output directory structure
- Save model results, content list, and Markdown output
- Exception handling and logging
Practical Application Scenarios
1. Academic Research
- Batch extract research paper data
- Build a literature knowledge base
- Extract experimental data and charts
2. Data Analysis
- Extract financial statement data
- Process technical documents
- Analyze research reports
3. Content Management
- Document digital conversion
- Build a search system
- Build a knowledge base
4. Development Integration
- RAG system development
- Document processing service
- Content analysis platform
Performance Optimization Suggestions
- Memory Management
- Control the number of concurrent processes when batch processing
- Clear temporary files in time
- Use generators to process large files
- GPU Usage
- Select an appropriate batch size
- Monitor GPU memory usage
- Adjust model precision according to needs
- Output Optimization
- Select an appropriate output format
- Compress images to save space
- Use incremental saving to avoid data loss
Common Problem Solving
1. Installation Issues
Q: Error: “No precompiled package found”? A: Check if the Python version is 3.10, and ensure the pip source is configured correctly.
2. Recognition Issues
Q: Complex formula recognition is inaccurate? A: Try using the high-precision mode, and ensure the PDF quality is good.
3. Performance Issues
Q: Processing large files is slow? A: Enable GPU acceleration and adjust the batch size appropriately.
More Articles
![OpenAI 12-Day Technical Livestream Highlights Detailed Report [December 2024]](/_astro/openai-12day.C2KzT-7l_1ndTgg.jpg)